Lobe Pump
What is Pump?
A pump is a mechanical device that transfers a liquid or gas from one place to another. The pump moves a fluid by creating a pressure difference by providing energy.
What is lobe pump?
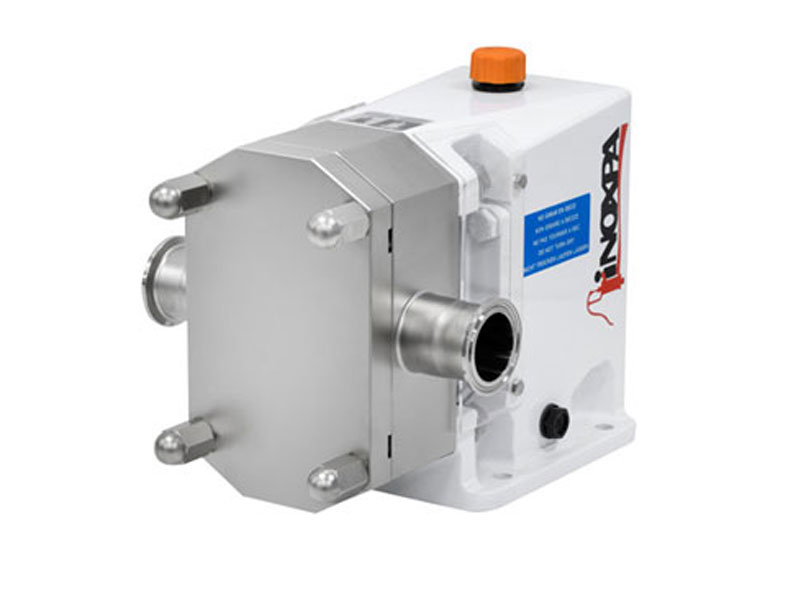
A lobe pump is a type of positive displacement pump used to move liquids or gases under high pressure. It consists of symmetrically shaped lobes (curtains) arranged on two or more parallel rotating axes. The lobes are placed in such a way that they form a space separated from each other without touching each other or the inner wall of the pump.
A lobe pump is a type of positive displacement pump generally used to transport viscous or dense liquids. It has a design in which rotors with two or more lobes are placed parallel to each other. Each of these rotors is equipped with lobes and forms a telescoping configuration. The rotors rotate so that they do not touch each other and create a gap to pump the fluid.
The lobe pump captures the fluid from a space between lobes that do not functionally touch each other and advances the fluid by pushing this space with the rotation of the rotors. As the rotors rotate, each lobe chamber is filled from the suction side and moves towards the pressure side. This process ensures a continuous advancement of the fluid.
Lobe pumps are generally used to transport viscous liquids, pastes, gelatinous substances, creams, dough, adhesives, oils, chemicals and other similar materials. They are widely used in many industries such as food processing, pharmaceutical manufacturing, chemical industry, petrochemical, cement production and wastewater treatment.
Lobe pump is a type of pump used for in-line transfer of low or high viscosity products or fluids containing solid particles. The lobe pump transports the products it transfers without damaging the structure or damaging the product.
Lobe Pumps Overview

Lobe pumps are used in a variety of industries such as pulp and paper, chemical, food, beverage, pharmaceutical and biotechnology. They are frequently used in these different industries as they offer excellent sanitary properties, high efficiency, reliability, corrosion resistance, and clean-in-place and sterilize-in-place (CIP/SIP) properties.
Lobe pumps offer a variety of lobe options, including single, two-bladed, three-lobed and multi-lobed. Rotary lobe pumps are non-contact and have large pump compartments to avoid damaging products such as cherries or olives. They are also used to process slurries, pastes and a wide variety of other liquids. Lobe pumps offer self-priming performance if they get wet. A gentle pumping action minimizes product spoilage. They also offer reversible flows and can stay dry for a long time. Flow is relatively independent of changes in process pressure, so output is continuous and uninterrupted.
Rotary pumps, another lobe pump, are used in various sectors from industrial designs to sanitary designs. Healthy designs are further dispersed depending on the service and specific sanitary requirements. These requirements include 3-A, EHEDG, and USDA. The manufacturer can tell you which certifications, if any, are met with their rotary lobe pumps.
How Lob Pumps Work
Fluid passing through the lobe pump. Lobe pumps are similar to external gear pumps that are actuated in that this fluid flows around the casing. However, unlike external gear pumps, the lobes do not make contact. Lobe contact is blocked by external timing gears in the gearbox. Pump shaft support bearings are contained within the transmission and bearings are outside of the pumped fluid, limited by pressure, bearing position and shaft deflection.
As the lobes exit the cage, they create an expanding volume on the inlet side of the pump. The fluid flows into the cavity and is trapped by the lobes as they rotate.
- The fluid circulates around the stem in pockets between the lobes and the stem – it does not pass between the lobes.
- Eventually, the sticking of the lobes together delivers fluid under pressure from the outlet hole.
Lobe pumps are frequently used in food applications as they handle solids without damaging the product. The particle size pumped may be larger in lobe pumps than in other types of PD. Because the lobes do not touch and the gaps are not as close as other PD pumps, this design handles low-viscosity fluids with reduced performance.
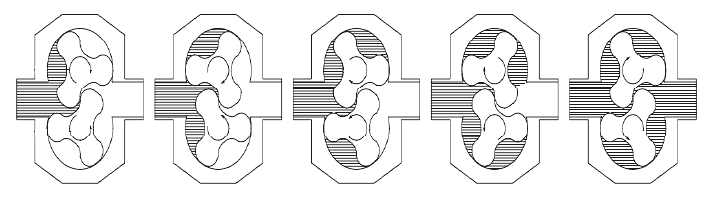
How Lobe Pump Works
Its loading characteristics are not as good as other designs and its absorption ability is low. High viscosity fluids require low speeds to achieve satisfactory performance. Reducing 25% of the rated speed and below is common for high viscosity fluids.
Advantages of Lobe Pumps
- The inlet and outlet directions of lobe pumps are integrated into the process in the desired direction (right-left).
- Transfers solid particles in the fluid without damaging them
- Transfers fluid smoothly, stably and linearly
- Can be used in applications requiring high temperatures
- It operates at low speeds and carries the fluid without tiring or flapping.
- Integrates into the line with different connection types without changing the connection type in the process (DN, RJT, SMS, Clamp)
- Easy to clean
- Easy to maintain
- Thanks to its compact design, it provides a great advantage in terms of space.