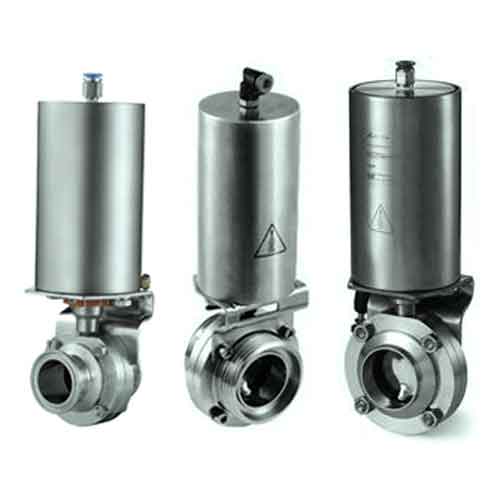
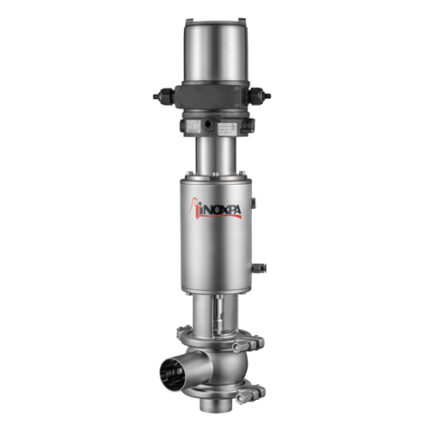
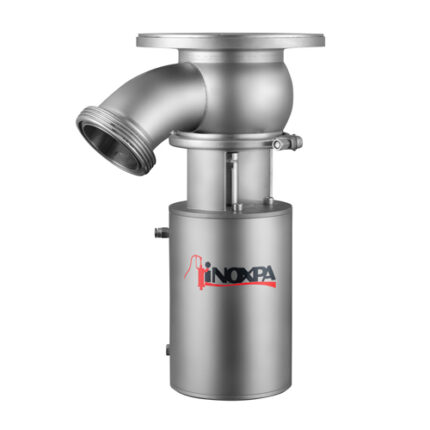
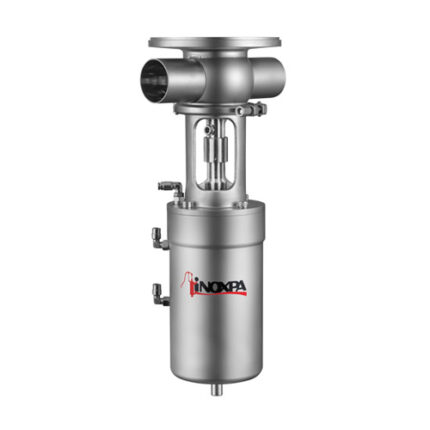
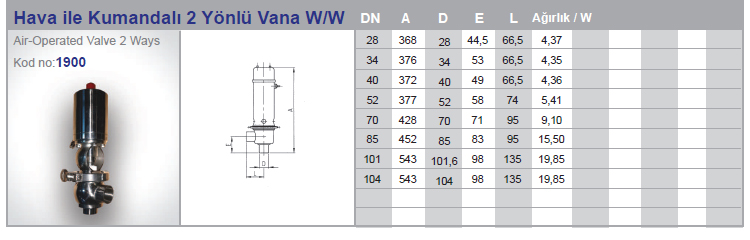
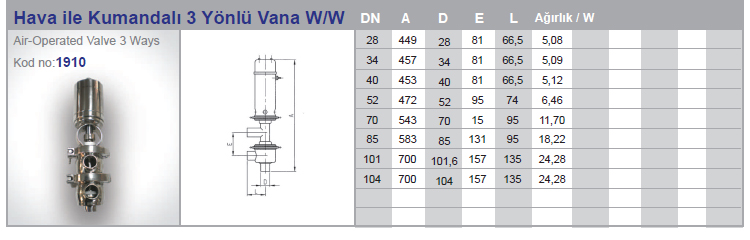
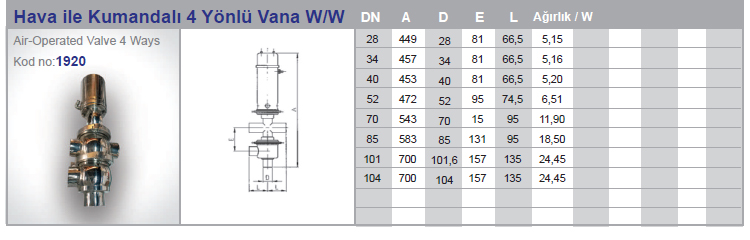
Air Operated Valves (Pneumatic valve)
Air Operated Valves (Pneumatic valve) is a type of powered valve that uses compressed air to operate the valve mechanism. It typically consists of a pneumatic actuator that converts energy from compressed air into mechanical motion and a valve body that controls the flow of liquid or gas in the system. Air Operated Valves are commonly used in industrial applications where hazardous or explosive substances may be present, as they can be remotely controlled and do not require electrical power.
Air Operated Valves (Pneumatic Valves)
Air operated valves are powerful pipe valves used in pneumatic systems and designed to control air pressure. They function like solenoid valves and act using air pressure. Compressed air is forced against a piston or diaphragm wall to initiate movement of the valve, while the valve closes when the pressure decreases.
 Pneumatic valves are widely used in various industrial applications. They are ideal for many functions, especially in pneumatic systems.
Pneumatic valves are widely used in various industrial applications. They are ideal for many functions, especially in pneumatic systems.
Main usage areas of Air Operated Valves (Pneumatic valve):
- Activating System Components: When a certain pressure is reached, valves activate a specific part of a system, moving equipment. For example, they can be used for operations such as starting a machine part or opening a coating.
- Pressure and Flow Control: Valves can be used to maintain a constant pressure or flow rate within the system. Additionally, when the pressure reaches excessive levels, the valve releases the pressure, preventing damage to the system.
There are various types of air operated valves, they are designed according to different applications. For example, there are types such as one-way valves, two-way valves, pressure regulators and flow control valves.
Air operated valves are an important type of valve used reliably in pneumatic systems and serve many industrial functions. It both ensures the correct operation of equipment and prevents damage to the system, increasing the efficiency and safety of industrial processes.
How do Air Operated Valves (Pneumatic valve) work?
Air Operated Valves work by using compressed air to actuate a piston or diaphragm, which opens or closes the valve. When compressed air is supplied to the actuator, it creates pressure that moves the piston or diaphragm and causes the valve to open and close. The amount of pressure applied determines how much the valve opens and closes. Air-operated valves are commonly used in industrial applications where electricity is not readily available or unsafe to use.
 Air operated valves work by using compressed air to move a piston or diaphragm, which opens and closes the valve. The working principle of these valves is quite simple but they function effectively.
Air operated valves work by using compressed air to move a piston or diaphragm, which opens and closes the valve. The working principle of these valves is quite simple but they function effectively.
When compressed air is supplied to the actuator, this pressure moves the piston or diaphragm. The piston or diaphragm moves the mechanical part of the valve, allowing the valve to open or close. The amount of pressure determines how far the valve will open or close. In this way, air-operated valves are provided with flow control.
Air-operated valves are commonly preferred in industrial environments where electricity is unavailable or unsafe. In this case, the valves can be operated with a simple air supply, eliminating electrical concerns.
In general, the use of air-operated valves
provides reliable and effective flow control in industrial facilities. They are preferred in many different industrial applications due to both their simplicity and durability. These valves help businesses make their processes more efficient while also increasing safety standards.
Usage areas of pneumatic valves
Pneumatic valves have various industrial and commercial uses. These include:
- Automation Industry: Pneumatic valves are widely used in automation systems. In factory automation, assembly lines, robotic applications and other automatic control systems, pneumatic valves are commonly used to control the movement of equipment.
- Food and Beverage Industry: In the food and beverage industry, where hygienic standards are important, pneumatic valves are used in processes such as transportation, dosing and mixing of liquid and solid materials.
Packaging Industry: In packaging machines, pneumatic valves are used in processes such as cutting, shaping, filling and sealing packaging materials. - Power Generation: In power plants, pneumatic valves are used to control gas, vapor and liquid flows. In power generation facilities, durable pneumatic valves, which are generally used in high pressure and high temperature applications, are preferred.
- Chemical Industry: In chemical plants, pneumatic valves are used to transport, mix and process various chemicals. These valves are made of chemically resistant materials and are resistant to aggressive chemicals.
- Automotive Industry: In automotive manufacturing plants, assembly lines, and test equipment, pneumatic valves are used to assemble and test vehicles.
- Water and Wastewater Treatment: In water and wastewater treatment plants, pneumatic valves are used to control the flow of water, direct filtration processes and treat wastewater.
- Aerospace Industry: In the aerospace industry, pneumatic valves are used to control different systems in aircraft, rockets and spacecraft.
These areas are just a few examples where pneumatic valves are used. Pneumatic valves are used reliably and effectively in many industrial applications.
Related products
2-Ways Plug Cock
3-Ways Plug Cock
Flow Control Valve
Hygienic Ball Valve
A Hygienic ball valve is a type of valve that controls flow along the line in a perforated and rotating sphere. These are the valves that work with the principle of moving the arm on the ball valves by 90°. Flow occurs when the perforated part on the Sphere in the ball valve is brought to the position to be in the same direction as the flow direction. Flow is restricted by moving the lever 90° from this position.