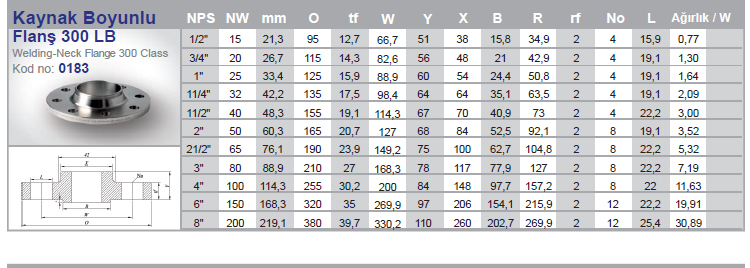
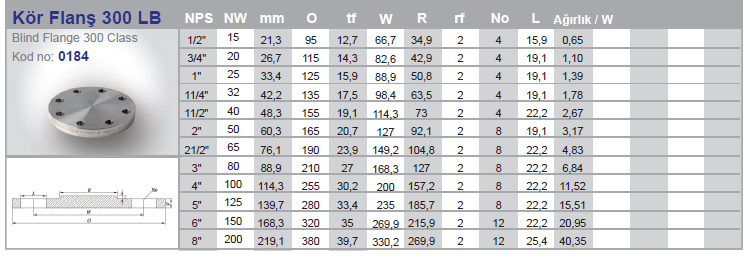
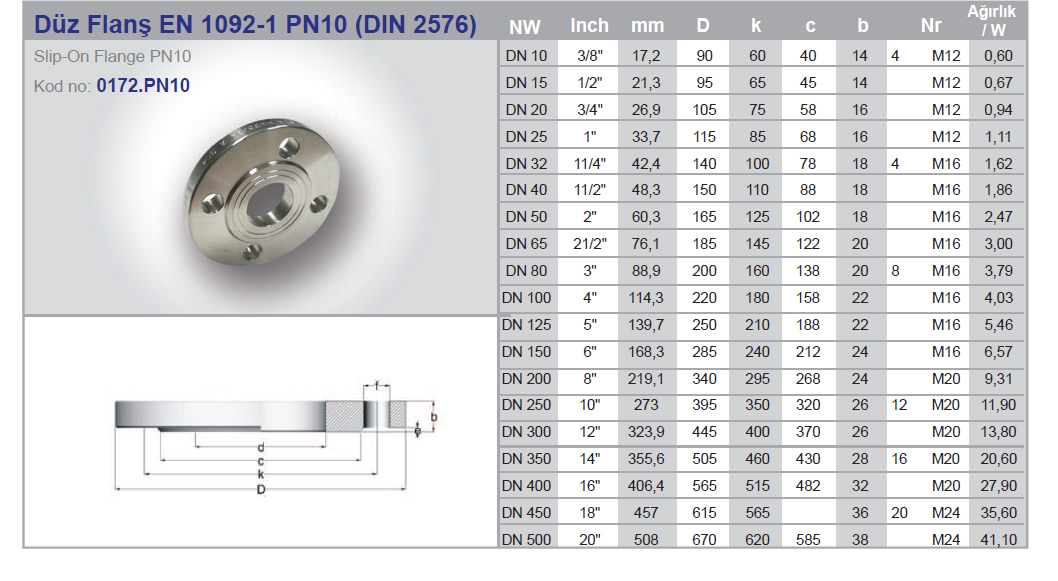
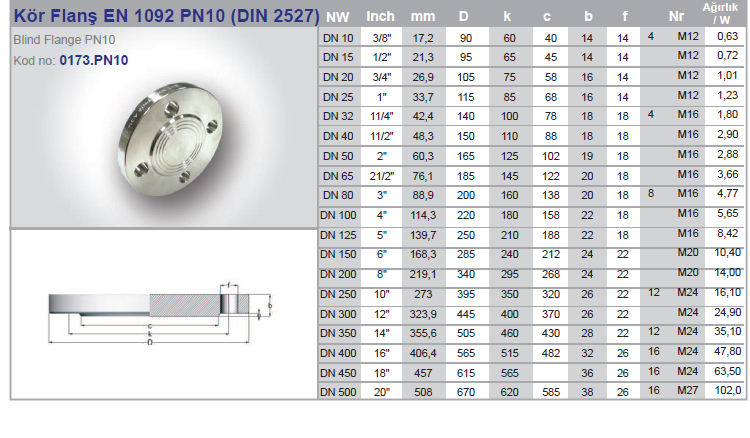
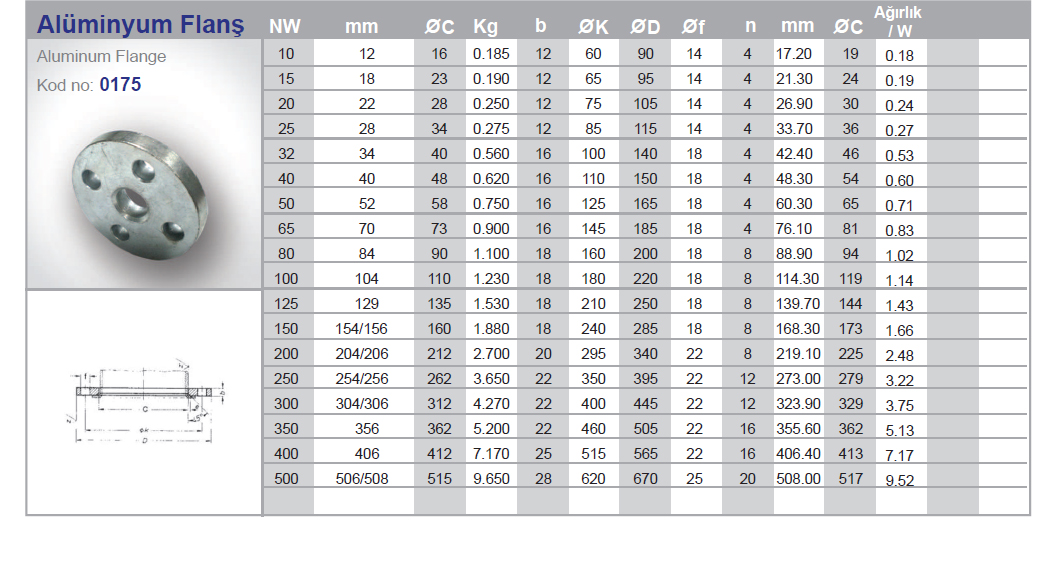
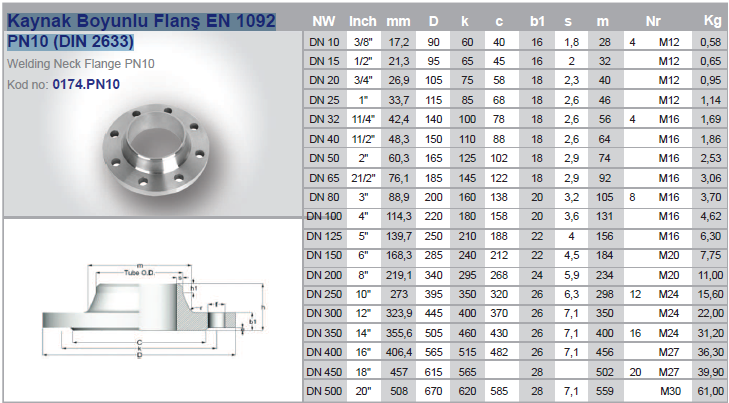
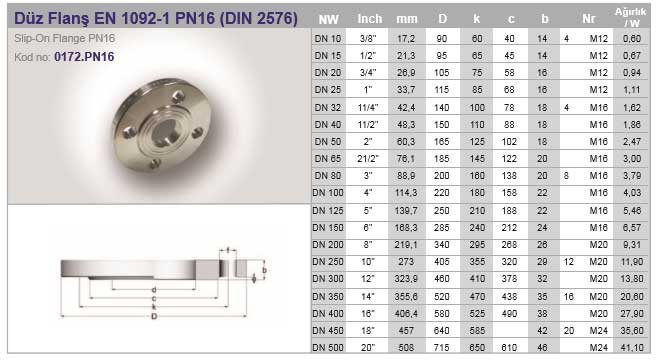
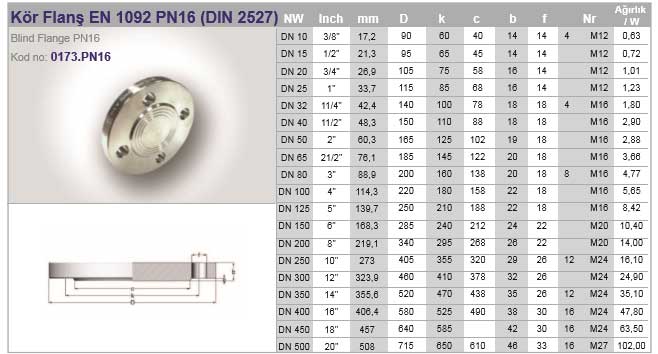
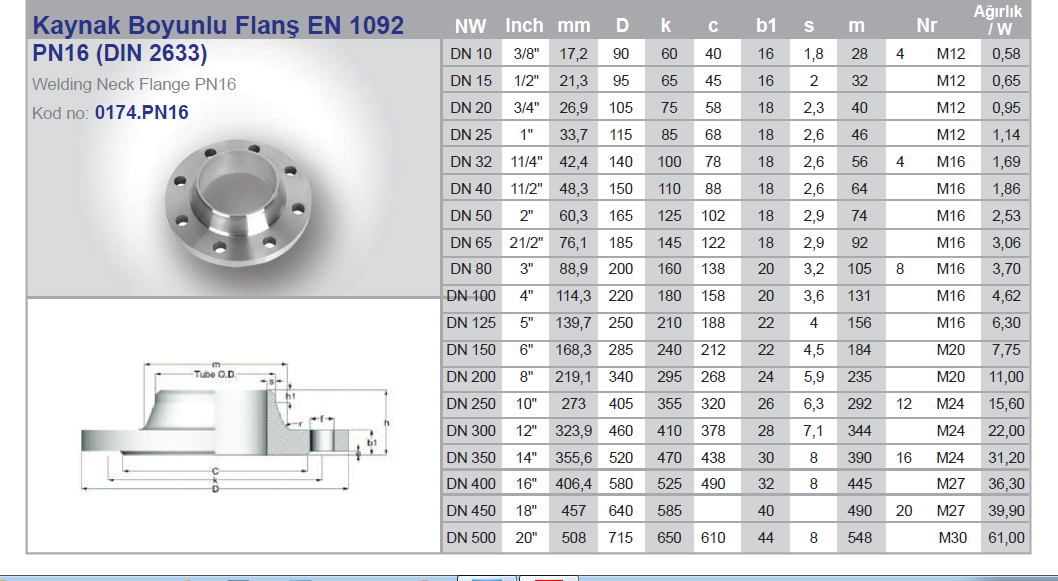
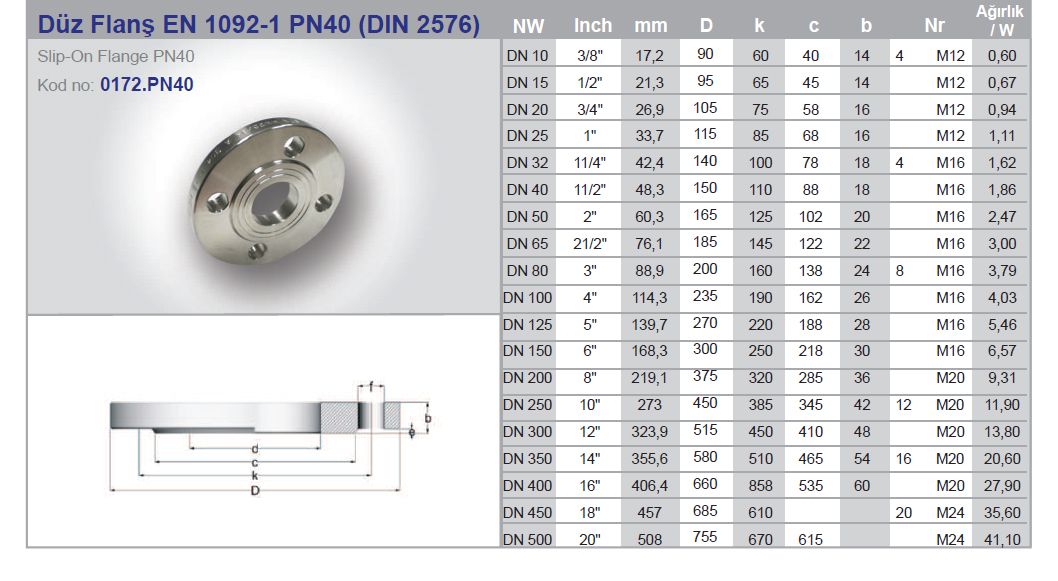
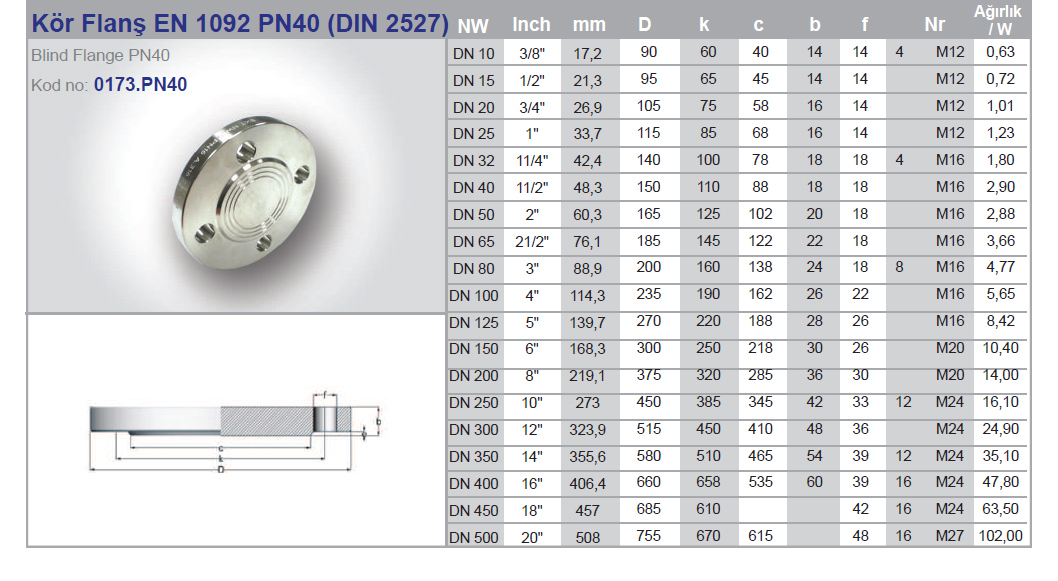
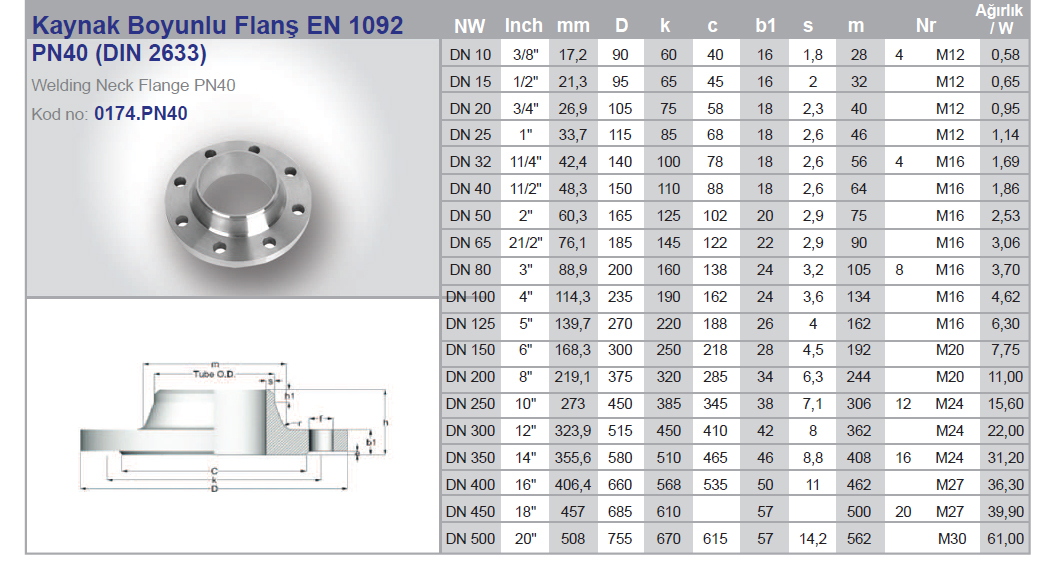
Flanges
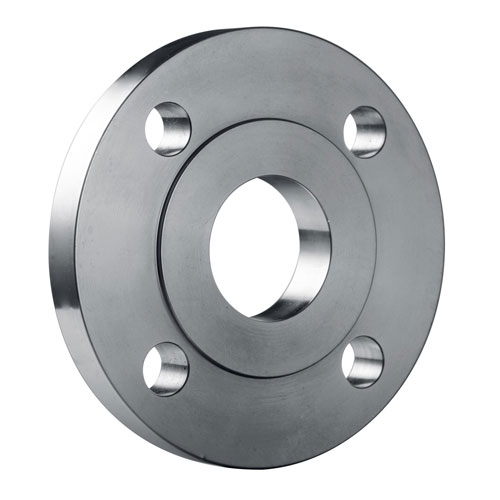
Stainless Flanges; It is a stainless fittings material that provides leakproof joining of parts in pipelines and various machines. Stainless flanges are generally used in pressurized environments. Flanges are sealed with gaskets used against pressure.
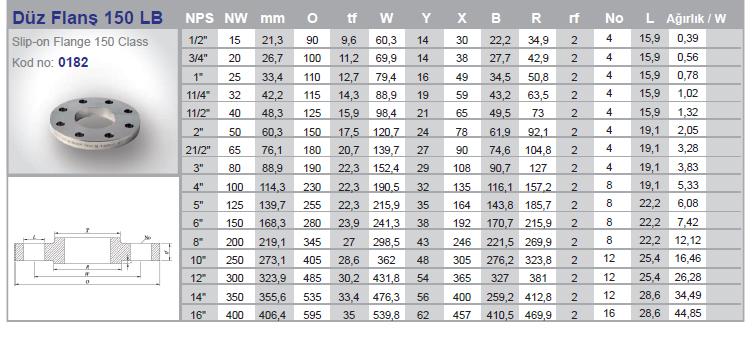
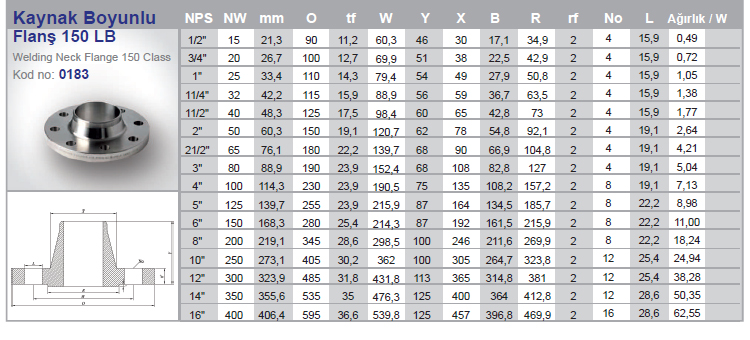
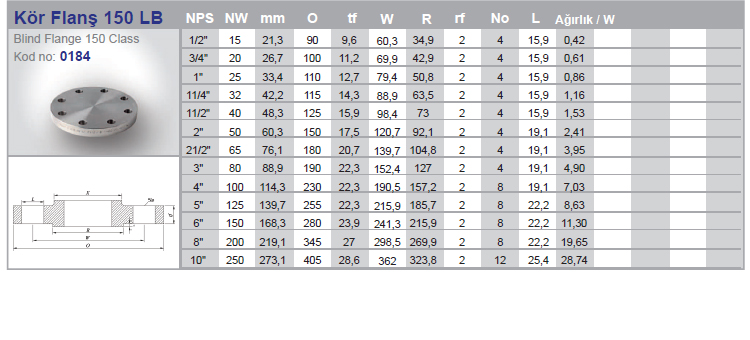
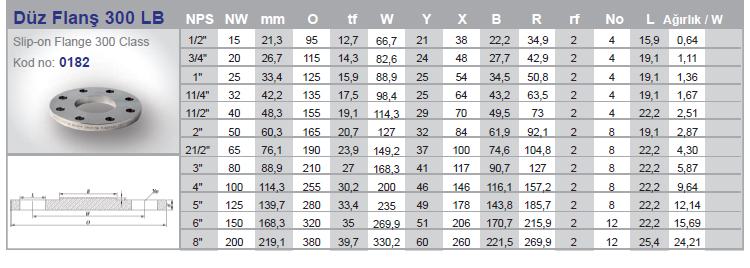
The stainless flange is a connecting element that allows two pipes to be connected to each other with the help of bolts in a way that they will weld to the pipe end in the pipelines. The reason for using a flange is that when any change in the pipeline is required, it can be changed by simply removing the flange connections without damaging the pipes and the pipeline.
In use, there are different types of flanges produced according to many different standards and within these standards. During the design of the installation, the following information is needed to determine the flange to be used;
- What is the Main Material?
- What is the corrosion status of the environment?
- What will the pressure of the system be?
- What will the temperature of the system be?
- What will be the purpose of the flange? (blinding, pipe connection, socket welding, use with collar, etc.)
When these issues are determined, the most suitable flange for our installation is selected. Although there are many different standards of stainless flanges being applied around the world, generally two different standards are focused on. These ;
- ASME Standards (American Standards)
- EN – DIN Standards (European Norm and German Norm)
In the American standard ASME, the sign ( # ) appears instead of PN. Examples such as 150# , 300# determine flange pressure classes to ASME Standards. If we examine it in a very general way, we can say that PN16 can withstand higher pressures than PN10.
The EN Standard is usually a classification according to the pressure class. PN10, PN16 etc. The expression PN here means Pressure Number in English.