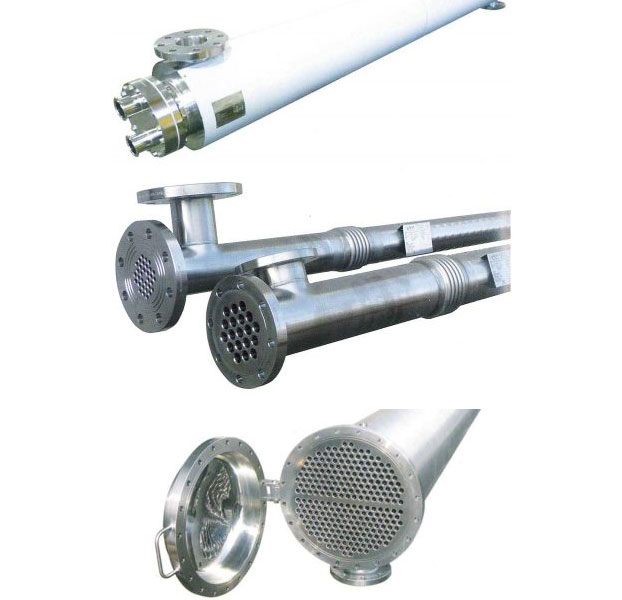
Tubular Heat Exchangers
What is a tube heat exchanger?
Tubular heat exchangers are device generally used for heat transfer. It is widely used in many industrial applications and in heating, ventilation and air conditioning systems. Tubular heat exchangers provide energy transfer by transferring the heat of a fluid (usually liquid or gas) into another fluid. These exchangers are usually arranged in a tubular shape and designed to maximize the surface area where the fluids come into contact with each other. This surface area is used to optimize heat transfer.
Tubular heat exchangers are used in various applications such as temperature control, heat recovery and steam production in industrial processes. For example, transferring the hot water in a boiler to a system used to heat the water with the help of a tube heat exchanger. This can save energy and increase process efficiency.
Types of tube heat exchangers:
Tubular heat exchangers can be found in different types according to various structures and usage purposes. Here are some common types of tube heat exchangers and their intended uses:
- Straight Tube Heat Exchangers: In this type of exchangers, the pipes are arranged in a straight manner. It is a typical type of heat exchanger in which liquids or gases come into direct contact with each other.
- Double Pipe Heat Exchangers: This type of exchangers, which are in contact between two pipes, enable the transfer of one fluid to another. Heat transfer between two fluids is ensured.
- Coated Tube Heat Exchangers: This type of heat exchangers are made by using another pipe placed inside a pipe. Heat transfer between two fluids occurs through the contact between the fluid circulating in the inner tube and the outer tube.
- Condensers and Evaporators: Condensers are used to convert vapor into liquid while evaporators are used to convert liquid into vapor. Both can be designed as tube heat exchangers.
- Air Cooled Exchangers: In these exchangers, the pipes are arranged in a structure through which a fluid is passed and air is blown outside. These types of exchangers are generally used for cooling liquids.
- Jacketed Tube Heat Exchangers: These are exchangers with a gap between the inner tube and the outer tube. This gap increases thermal insulation or allows the external fluid to heat or cool the internal fluid.
Each of these variants is designed to meet specific industrial or application requirements. It is used in various processes such as heat transfer, cooling, heating, and processing of liquids or gases.
Types of tube heat exchangers according to the sector in which they are used:
Pharmaceutical Industry Tubular Heat Exchangers – PSTE
 In the pharmaceutical industry tubular heat exchangers are important equipment used for various purposes. These exchangers are used in processes such as cooling, heating, evaporating or condensing liquids or gases during the pharmaceutical production process. Tubular heat exchanger types are used in the pharmaceutical industry to improve product quality, increase process efficiency and reduce production costs. Moreover, with their hygienic design, they can be made suitable to meet hygiene standards in pharmaceutical production.
In the pharmaceutical industry tubular heat exchangers are important equipment used for various purposes. These exchangers are used in processes such as cooling, heating, evaporating or condensing liquids or gases during the pharmaceutical production process. Tubular heat exchanger types are used in the pharmaceutical industry to improve product quality, increase process efficiency and reduce production costs. Moreover, with their hygienic design, they can be made suitable to meet hygiene standards in pharmaceutical production.
Food Industry Tubular Heat Exchangers – FSTE
In the food industry tube heat exchangers are important equipment used for functions such as temperature control, heat transfer and cooling of products in various processes. These exchangers are widely used in many processes such as food processing, pasteurization, sterilization, condensation and cooling. Here are some types of heat exchangers used in the food industry and their purposes:
 Heat Transfer Exchangers: These types of exchangers are used to provide heat transfer of foodstuffs. For example, temperature-regulated water or steam is used to control or process the temperature of the product.
Heat Transfer Exchangers: These types of exchangers are used to provide heat transfer of foodstuffs. For example, temperature-regulated water or steam is used to control or process the temperature of the product.- Pasteurization Exchangers: Pasteurization is the heating process of foodstuffs to kill harmful microorganisms or reduce their activity. Tubular heat exchangers are used for pasteurization of dairy products, fruit juices and other liquid foods.
- Sterilization Exchangers: Some foods need to be sterilized in order to be stored for a long time. Sterilization exchangers allow foodstuffs to be sterilized at high temperature and pressure.
- Cooling Exchangers: It is important to cool hot processed food products. Cooling exchangers cool products using evaporation, cold water or refrigerants.
- Condensers: Condensers are used to concentrate or remove water from food products. For example, condensers can be used in the process of making fruit juice concentrates.
- Hygienic Heat Exchangers: It is important that the heat exchangers used in the food industry are hygienic. Hygienic exchangers ensure food safety with their special structures designed for easy cleaning and sterilization.
Tubular exchangers used in the food industry are generally made of stainless steel and must comply with the standards of regulatory agencies such as the FDA. These exchangers play an important role in improving product quality, improving process efficiency and reducing production costs.
Industrial Tube Heat Exchangers – ISTE
 Industrial tube heat exchangers are important equipment generally used to provide heat transfer of liquids or gases. They are used in various processes in industrial facilities and have a wide range of applications. Tube heat exchangers generally have a structure in which a fluid passes inside the tubes and another fluid circulates outside. Heat transfer occurs thanks to the contact between two fluids. They are common types of tube heat exchangers used in various processes in industrial facilities. Each is designed to serve a specific purpose and plays a critical role in improving the efficiency of industrial processes.
Industrial tube heat exchangers are important equipment generally used to provide heat transfer of liquids or gases. They are used in various processes in industrial facilities and have a wide range of applications. Tube heat exchangers generally have a structure in which a fluid passes inside the tubes and another fluid circulates outside. Heat transfer occurs thanks to the contact between two fluids. They are common types of tube heat exchangers used in various processes in industrial facilities. Each is designed to serve a specific purpose and plays a critical role in improving the efficiency of industrial processes.
Working principle of tube heat exchangers
Pipe heat exchangers are devices that provide energy transfer by transferring the temperature of a fluid (usually liquid or gas) to another fluid. Its working principle is based on heat transfer caused by the temperature difference between two fluids. Here are the working principle steps of tube heat exchangers:
- Flow of Two Fluids: In the tube heat exchanger, there is generally a structure in which a fluid (hot fluid) passes through the tubes and another fluid (cold fluid) circulates outside. Both fluids circulate in different regions inside the exchanger.
- Heat Transfer: As the hot fluid circulates in the pipes, it comes into contact with the cold fluid through the pipe walls. Heat is transferred from the pipe walls of the hot fluid to the cold fluid. This causes the temperature of the hot fluid to decrease and the temperature of the cold fluid to increase.
- Control and Adjustment: Heat transfer is usually regulated through a control mechanism. This control is done to ensure the desired temperature difference and flow rate of the fluids. Thus, a certain heat transfer efficiency is achieved.
- Exit: The cold fluid exits the exchanger as it is heated as a result of heat transfer. The hot fluid loses heat by contacting the cold fluid and exits the exchanger at a lower temperature.
In this way, heat transfer between fluids in tube exchangers is used to change the temperature of a fluid or to transfer energy from one fluid to another. This principle is widely used in various processes such as heating, cooling, evaporation, condensation and pasteurization in industrial facilities.