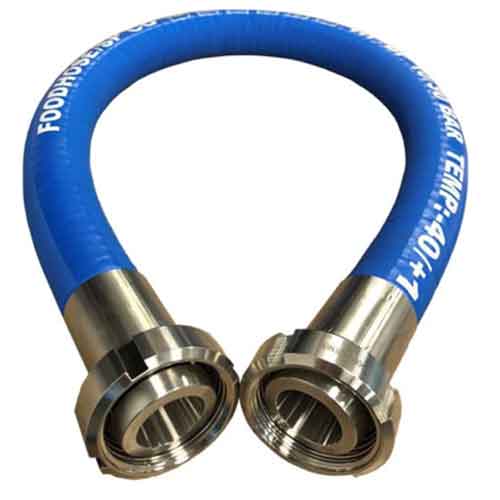
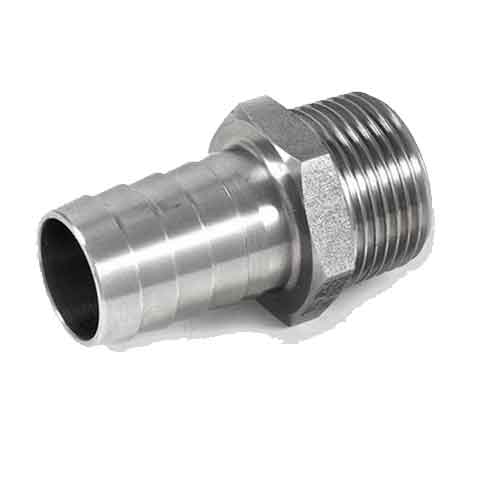
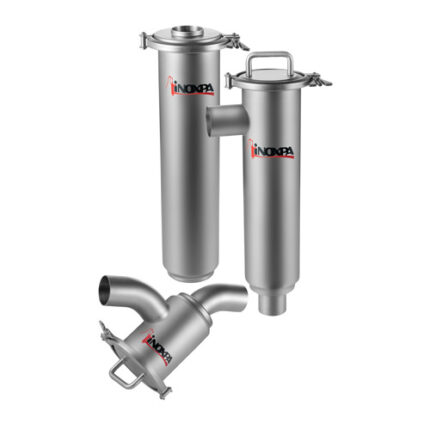
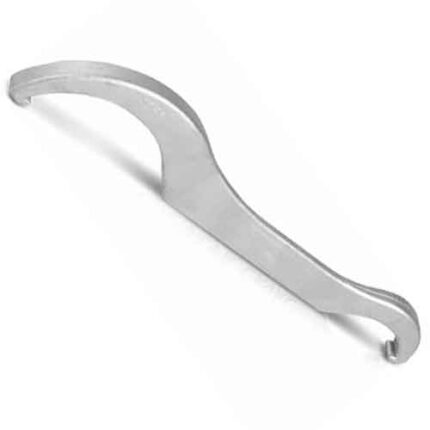
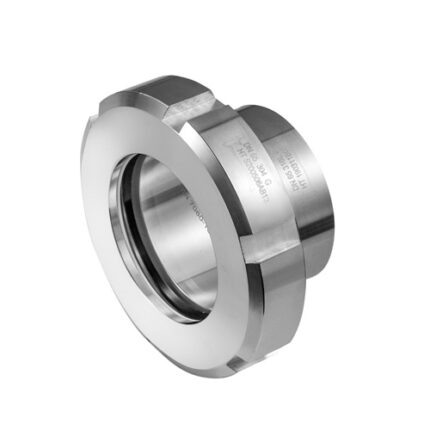
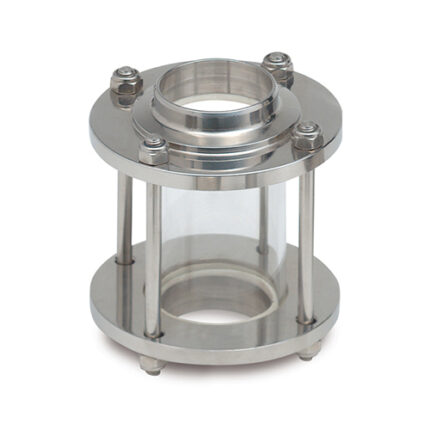
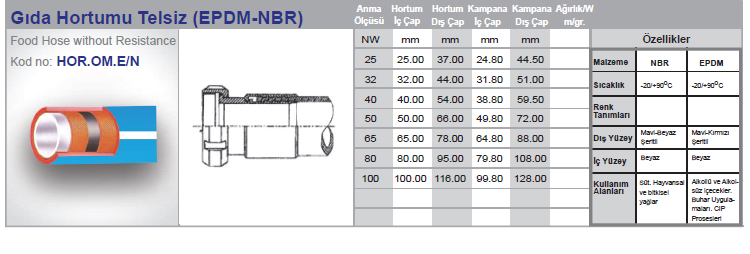
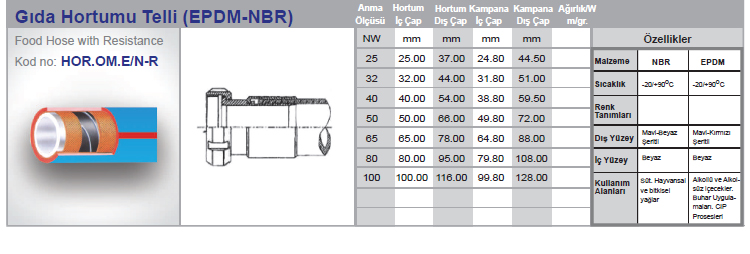
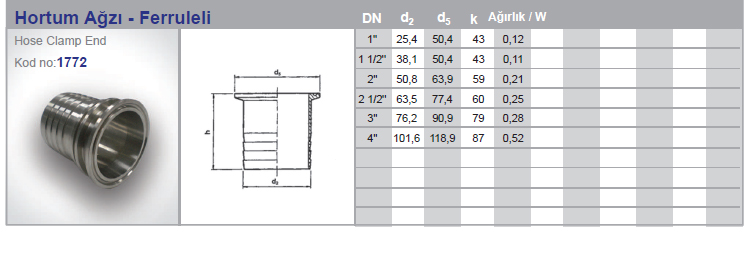
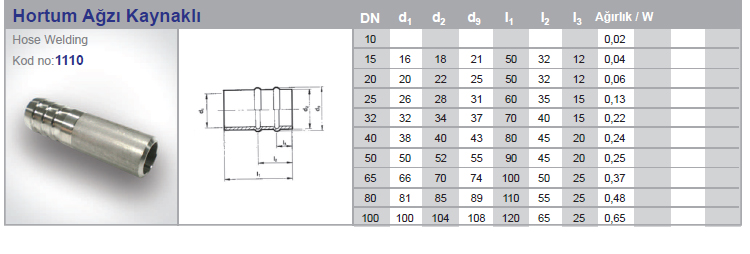
Hose Connection Part
Hoses are materials used to transfer liquids and gases from one environment to another without dispersal. Mostly rubber hoses and silicone hoses are widely used in industry.
Hoses are a flexible, hollow tube designed to move liquids from one location to another. Hoses are also sometimes called pipes (the word pipe usually refers to a rigid pipe, whereas a hose is usually flexible) or more generally pipes. The shape of a hose is usually cylindrical (it has a circular cross section).
Hose design is based on a combination of application and performance. Common factors are size, pressure rating, weight, length, straight tubing or coiled tubing, and chemical compatibility.
Applications often use nylon, polyurethane, polyethylene, PVC, or synthetic or natural rubbers, depending on the environment and the degree of pressure needed. In recent years, hoses can also be produced from special grade polyethylene (LDPE and especially LLDPE). Other hose materials include PTFE (Teflon), stainless steel and other metals.
Application
Hoses can be used in water or other liquid media, or to transport air or other gases. Hoses are used to transport fluids in air or fluid environments and are typically used with clamps, spigots, flanges and nozzles to control fluid flow.
Hose Types
Rubber hose is widely used in conveying systems for both pipeline and elbows and in systems where some degree of inherent flexibility is required. Its special properties make it ideal for use in systems where the conveyed material may be friable, abrasive or sticky.
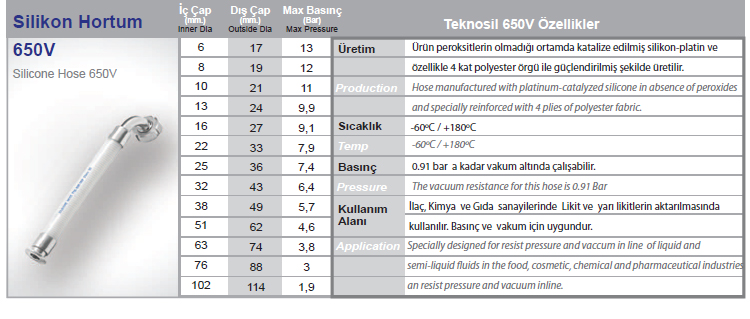
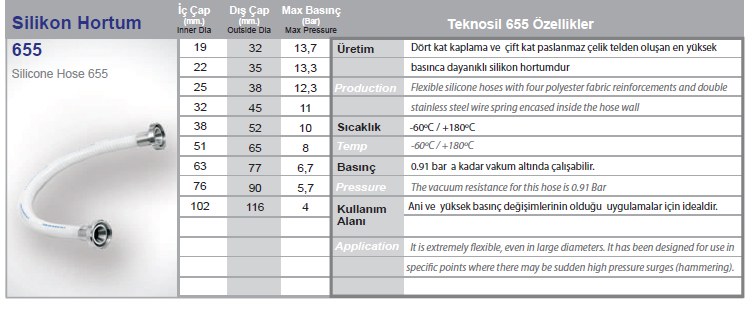
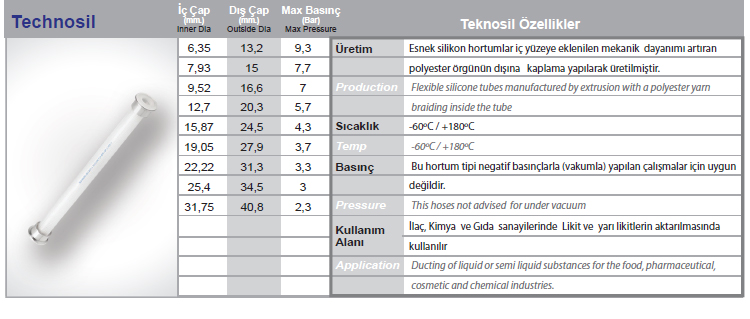
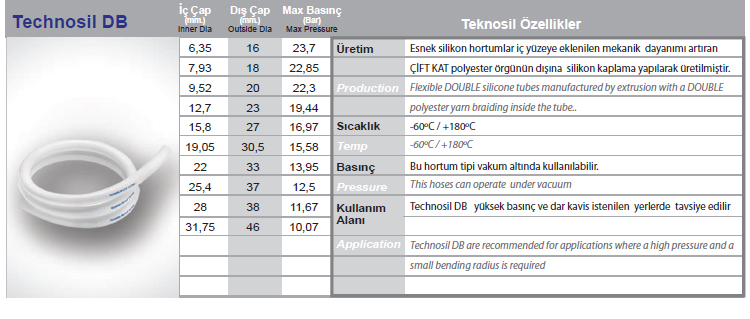
Silicone hose refers to a family of flexible tubes or tubing made of various silicone rubber formulations. These products exhibit the unique properties of silicone materials, including a wide range of operating temperatures, flexibility, stability and resistance to many chemicals.