Hybrid Heat Exchanger – All Welded Design
Hybrid Heat Exchangers (Welded Heat Exchangers) –; Based on a very flexible configuration platform, the Hybrid is designed to operate under harsh conditions where other heat exchanger technologies can fail, have a shorter operating life, or reduce operational efficiency.
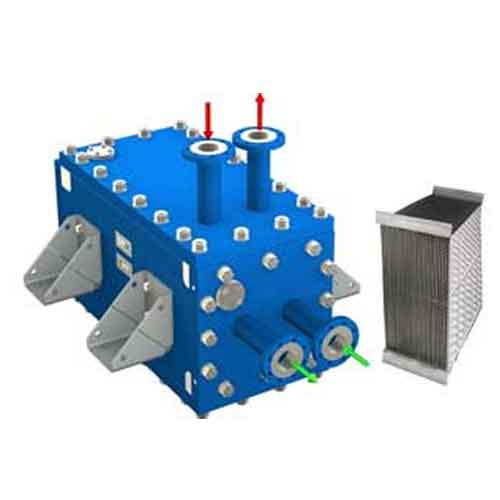
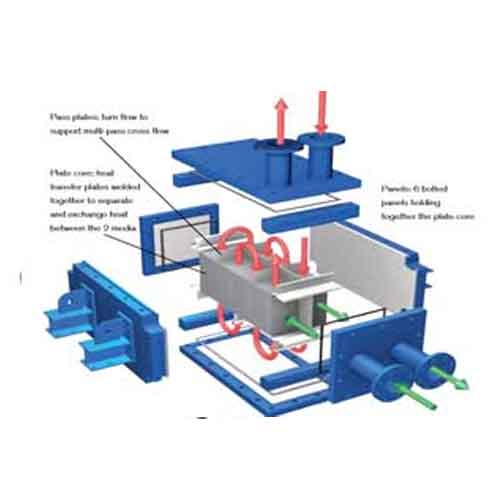
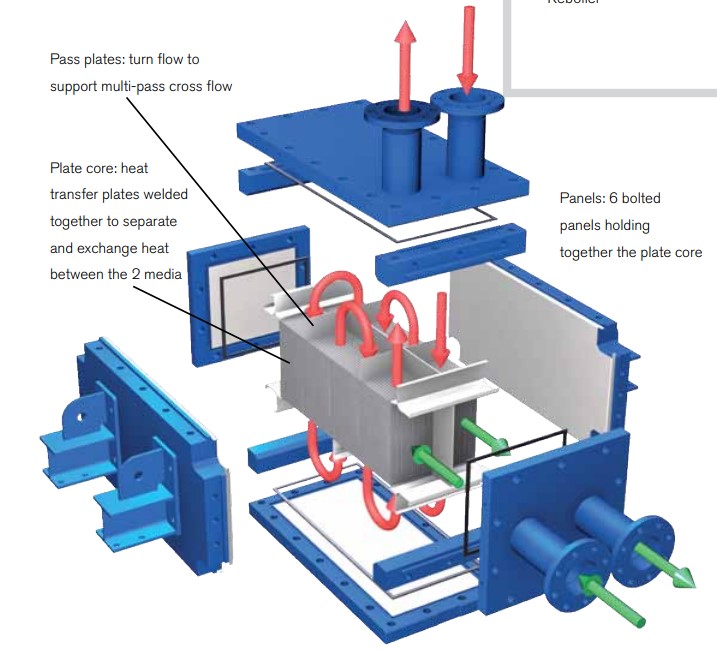
Hybrid – Welded Heat Exchanger, easy access Makes high pressure cleaning of hybrid plates simple, effective and fast!
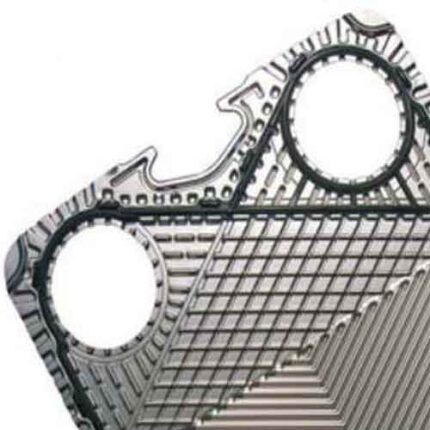
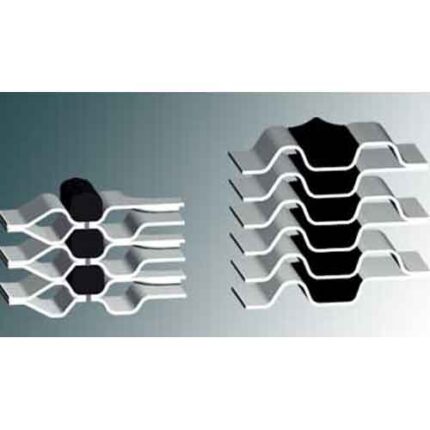
The fully welded heat exchanger Hybrid Heat Exchanger consists of high efficiency plates and a strong channel structure. It is designed to operate under difficult conditions where extremely low pressure loss is required, if necessary, where other heat exchangers cannot perform due to temperature and pressure limitations. Thanks to its compact and flexible design, the APV Hybrid takes up 5-10 times less space than conventional tube heat exchangers that perform the same tasks.
Hybrid Heat Exchanger Application areas:
It is generally used at high temperature and high pressure for heating, cooling, condensation and evaporation. E.g; used in energy, chemical, petrochemical and sugar industry applications.
Welded Heat Exchanger Application:
- Oil and Gas
- Gas sweetening
- Gas Dehydration
- Crude oil stabilizer
- Crude oil heater
- Chemical
- Solution cooler and heater
- Process condenser
- Cryogenic chiller
- Power
- Steam condenser
- District heating units
- Industrial
- Reboiler
Materials
Plates: AISI 316L or many alloys
Main Body: AISI 316L or carbon steel
Temperature: Operating temperature, PED 97/23 EK: -40°C to 350 °C Operating temperature, ASME VIII: -28 °C to 350 °C
Pressure: -1 _32 bar
Heat transfer area / Capacity: Up to 436 m2 in each unit
Maintenance: Full cleanability and fixation without removing the pipe connections. More cleaning possibilities with the CIP system
Design Pressure: 232.1 or 464.1 psig (16 or 32 Bar)
Design Code: ASME VIII, Div 1 or PED
Design Temperature: -18.4/-40 to 662°F (-28/-40 to 350°C)
Advantages:
- High efficiency
- High capacity
- Low pressure loss
- It is extremely flexible
- Easy maintenance and observation
- Low maintenance costs
- Less space
How do welded heat exchangers work??
 Welded heat exchangers are heat exchangers designed to produce hot water using hot water from a combi boiler or boiler as the primary heating source, as well as solar energy, a hot water tank or another heat source. Such exchangers are also called “hybrid exchangers”.
Welded heat exchangers are heat exchangers designed to produce hot water using hot water from a combi boiler or boiler as the primary heating source, as well as solar energy, a hot water tank or another heat source. Such exchangers are also called “hybrid exchangers”.
Features of Welded Heat Exchangers:
- They have dual heat sources, usually a gas or electric powered main heater and a source such as solar power or a hot water tank as an alternative heat source.
- They have two separate circuits: a primary heating circuit and a secondary heating circuit.
- They first produce hot water from the primary source, but can also supply hot water from an alternative source when needed or if the primary source is unavailable.
- Control systems often take into account various factors (e.g. sunlight level, hot water demand, outside air temperature, etc.) to decide which source to use.
Usage Areas of Welded Heat Exchangers:
- Houses: They can be used to provide hot water in homes, improving energy efficiency by utilizing both conventional energy sources (gas, electricity) and renewable energy sources (solar energy).
- Commercial Buildings: They can also be used for hot water supply in commercial buildings such as hotels, hospitals, schools.
- Industrial Applications: They can be used in industrial plants, especially for process heating.
Advantages of Welded Plate Heat Exchangers:
- Energy Efficiency: Increases energy efficiency by using multiple energy sources.
- Less Carbon Emission: Encourages the use of renewable energy sources and therefore reduces the carbon footprint.
- Reliability: Having two different energy sources allows the system to continue when one source fails or becomes unusable.
- Long-Term Savings: Provides long-term savings by providing less energy consumption and lower operating costs.
These features and advantages make welded heat exchangers preferred in various applications.