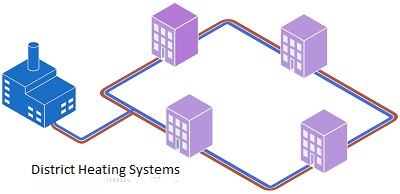
What is District Heating?
Before delving into the Use of Heat Exchangers in District Heating, we must define district heating. District heating is the process of heating usually in a specific area. With district heating, the heating and hot water needs of many buildings are met from a power plant or a different heat source such as geothermal water and industrial wastewater. This system is used to save energy, achieve better temperature control, or provide heating tailored to the needs of a particular space. District heating systems can be used in homes, offices, industrial facilities and many other areas. District heating has been used in various countries since the 14th century by circulating geothermal water within the city through pipes.
Use of Heat Exchangers in District Heating:
In district heating systems, heat exchangers are frequently used. A heat exchanger takes heat from a source through a fluid (usually water or steam) and uses it to heat another fluid (usually air or water within a building). In this way, district heating systems work efficiently.
Benefits of Using Heat Exchangers in District Heating:
- Energy Savings: District heating systems generally consume less energy than larger central heating systems. Because heat is provided only to a certain area.
- Better Control: District heating systems provide better control to meet different temperature requirements in different regions. This allows you to use energy more efficiently and increase comfort.
- Flexibility: District heating systems can be designed flexibly to provide heat to specific areas where it is needed. This ensures that users can only heat certain rooms or areas, thus avoiding unnecessary energy consumption.
Disadvantages of Using Heat Exchangers in District Heating:
- High Initial Cost: The installation cost of district heating systems is generally higher compared to central heating systems. This may be a disadvantage for initial investors.
- Maintenance Requirements: Since there are multiple district heating units, maintenance requirements may increase. It is important to maintain each unit regularly.
- Complex Installation: District heating systems generally require more complex installation and, as a result, require more planning and attention.
Exchangers Commonly Used in District Heating:
- Plate Heat Exchangers: Plate heat exchangers are known for their fast heat transfer and compact designs. Therefore, they are frequently used in district heating systems.
- Duct Heat Exchangers: Duct exchangers are generally used in ventilation systems and for heating the air or water inside the building.
- Tubular Heat Exchangers: Tubular heat exchangers are used to provide heat transfer of fluids between tubes. These exchangers are commonly used in larger facilities and industrial applications. Exchangers in District Heating
This provides an overview of the use, benefits and drawbacks of heat exchangers in district heating systems. Because each situation has unique requirements, correct exchanger selection and system design are important to maximize efficiency and performance.
Exchanger District Heating Units
If you do not want to waste time with valves, pumps and plate heat exchangers, then choose a central heating unit. Buy one unit instead of 15-20 pieces. Easy to install and takes a day. Just plug it in and get warm.
Since the 1970s, SPX has designed, developed, manufactured and maintained district heating units. With one or a thousand heating systems, SPX is a supplier of kilowatt-sized or solutions. Use of Heat Exchangers in District Heating
You can trust SPX’s experience for your district heating needs.
Benefits of Plate Heat Exchangers in District Heating
- Flexible size, performance and selection of components
- Applied according to your needs
- 9 standard types
- Comprehensive selection of Heat Exchangers (all welded, brazed, plate and body)
Use of Heat Exchangers in District Heating
- HVAC
 Stainless Steel Products
Stainless Steel Products Mixing
Mixing Pumps
Pumps Heat Exchangers
Heat Exchangers System Solutions
System Solutions