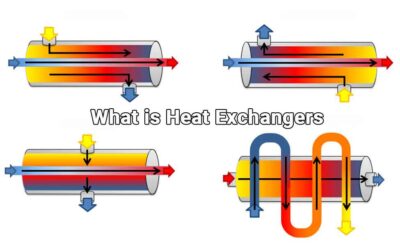
 Heat Exchanger:
Heat Exchanger:
What is Heat Exchanger? and How to Determine Heat Exchanger Prices: Heat Exchangers are devices that provide heat transfer between two or more fluids at different temperatures. These devices allow fluids to transfer heat from one to another without mixing.
In its simplest definition, a heat exchanger is a device that provides heat transfer from one medium to another. For example, a Hydraulic Oil Cooler uses cold water or air to remove heat from hot oil. Another example is the Swimming Pool Exchanger; This exchanger uses hot water from a boiler or solar-heated water mains to heat the pool water. Heat is transferred through exchanger materials and separates the media used. Plate or tube heat exchangers pass liquids through or over pipes, while air-cooled heat exchangers cool a liquid by passing cold air through a fin.
In heat exchangers, fluids are generally separated from each other by a heat transfer surface, thus preventing the fluids from mixing.
The usage areas of heat exchangers are quite wide. It is widely used in many industrial areas, from process industry to petrochemistry, from power plants to building heating-cooling systems, from air conditioning plants to ship construction.
The most common examples encountered in daily life include car radiators, split air conditioner coils, air heaters, domestic water heaters in combi boilers and oil coolers.
What is Heat Exchanger and what are its types?:
Heat Exchangers are generally divided into three categories: Tubular Heat Exchanger, Plate Heat Exchanger and Brazed Heat Exchangers.
Tubular Heat Exchanger:
Tubular heat exchangers are commonly used heat exchangers in facilities involving oil refineries and other large chemical processes. In these exchangers, heat transfer occurs through pipes. Pipes used for heat transfer can generally be straight or spiral shaped. While a fluid is passed through the pipes, another fluid circulates outside and thus heat transfer occurs. Tubular heat exchangers are known for their simple structure and effective performance.
Plate Heat Exchanger:
Plate heat exchangers are determined by the plate size and number of plates according to the flow rate of the fluid passing through them, physical properties, pressure drops, inlet-outlet temperature values and the desired maximum strength value. The ability to easily add and remove plates makes it easier to clean plate heat exchangers. Plate heat exchangers are determined by the plate size and number of plates according to the flow rate of the fluid passing through them, physical properties, pressure drops, inlet-outlet temperature values and the desired maximum strength value. The ability to easily add and remove plates makes it easier to clean plate heat exchangers. Plate exchangers are more efficient than tubular exchangers due to the highly turbulent flow. It is also lighter and cheaper.
Brazed Heat Exchanger:
Brazed heat exchangers have 25% more efficiency than detachable type heat exchangers and 10 times more efficiency than tube type heat exchangers. In addition to being smaller and lighter in size than tubular type exchangers, they can operate efficiently even with temperature changes of 1 °C.
 Heat Exchanger Prices
Heat Exchanger Prices
Heat exchangers are important equipment used in industrial processes and many applications requiring heat transfer. Exchanger prices vary depending on many factors and often vary based on specific features, dimensions and functionality.
Some main factors affecting heat exchanger prices are:
- Heat Exchanger Type and Material: Different designs such as tube, plate, spiral and different materials such as carbon steel, stainless steel and copper can be used. Material selection has a direct impact on the durability, heat transfer efficiency and functionality of the heat exchanger.
- Size and Capacity: The dimensions and heat transfer capacities of exchangers are an important factor that determines their prices. Larger sized exchangers generally cost more because they require more materials and manufacturing processes.
- Production Standards and Quality: For heat exchangers that are of good quality and comply with certain industry standards, the dimensions and heat transfer capacities of the exchangers are generally an important factor that determines their prices. Larger sized exchangers generally cost more because they require more materials and manufacturing processes. It is more costly with . Exchangers purchased from reliable manufacturers and well-known brands can often last longer and have lower operating costs.
- Assembly and Installation Costs: Assembly and installation of heat exchangers can increase the total cost. This includes factors such as plumbing requirements, installation labor and professional services.
- Market Conditions: Factors such as market demand, exchange rates, raw material prices and industrial demands can affect exchanger prices. Market conditions and supply-demand balance may cause fluctuations in exchanger prices.
As a result, heat exchanger prices can vary depending on many variable factors and are often determined by the requirements and budget of a particular project. Customers should evaluate carefully and compare different options when choosing the heat exchanger that best suits their needs. It is also important to consider long-term performance and operating costs.
 Stainless Steel Products
Stainless Steel Products Mixing
Mixing Pumps
Pumps Heat Exchangers
Heat Exchangers System Solutions
System Solutions