Learn about different types of heat exchangers such as gasketed, tubular, brazed, hybrid, and semi-welded, and their applications in various industries.
Showing all 10 results
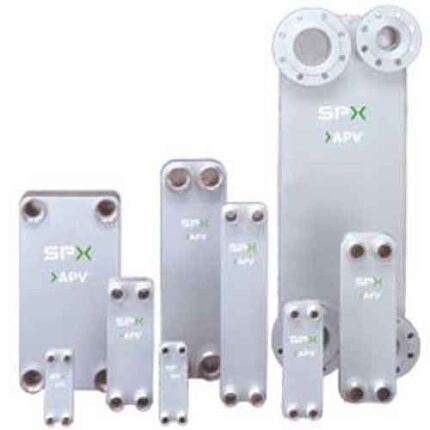
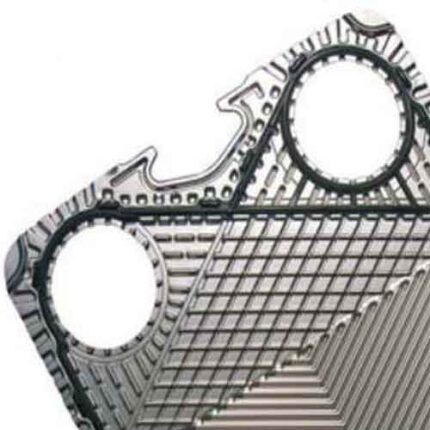
Gasketed – Hygienic Plate Heat Exchangers
Gasketed – Industrial Plate Heat Exchangers
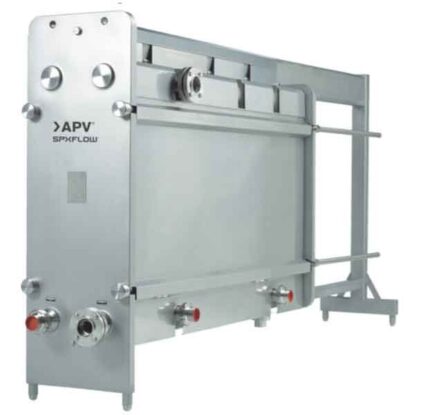
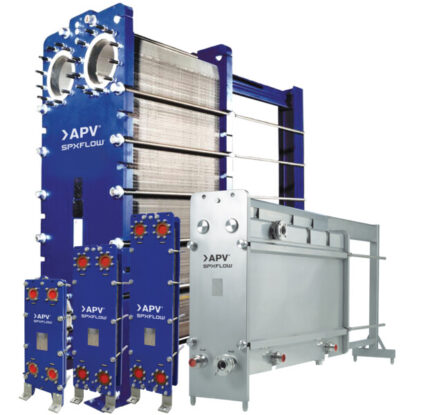
The global applications for industrial heat exchangers calls for a wide and deep product range, putting great demand on the equipment. SPX FLOW's portfolio of APV ParaFlow is designed to satisfy your needs, whether this is for very small flows, or the extra-large kind, up to 4500 m3/h. With our selection of materials, connections and accessories, we can supply equipment for practically every heat transfer need. The ParaWeld and Paramine technologies expand the boundaries for gasketed plate heat exchangers. Added our long experience in after sales services, SPX FLOW is your all-round partner for heat transfer.
Brazed Plate Heat Exchangers
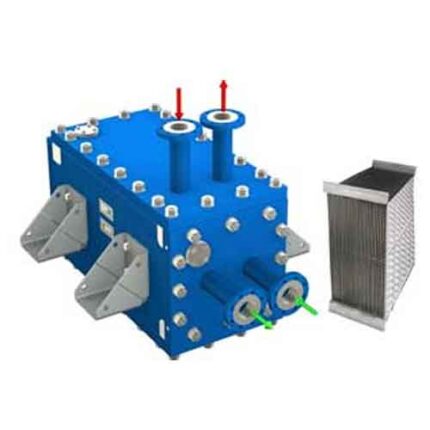
Hybrid Heat Exchanger – All Welded Design
Semi Welded Heat Exchanger – ParaWeld
APV Plates
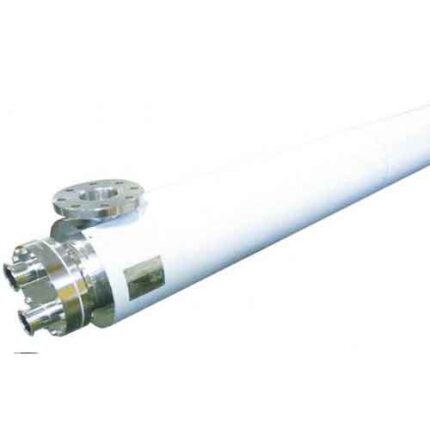
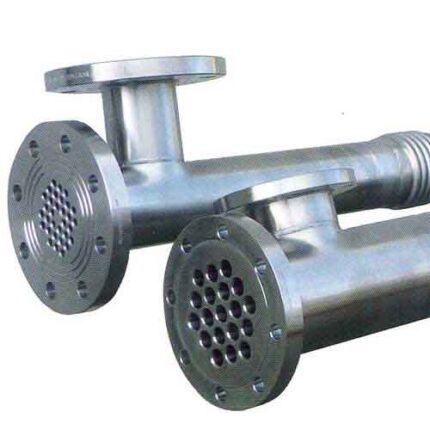
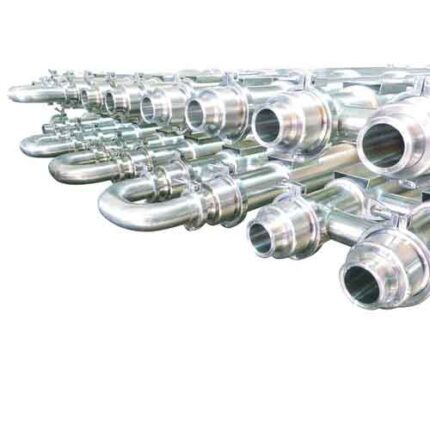
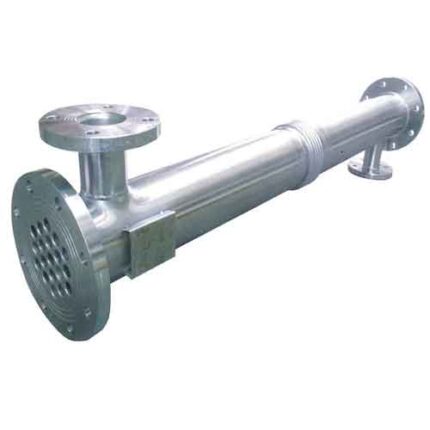
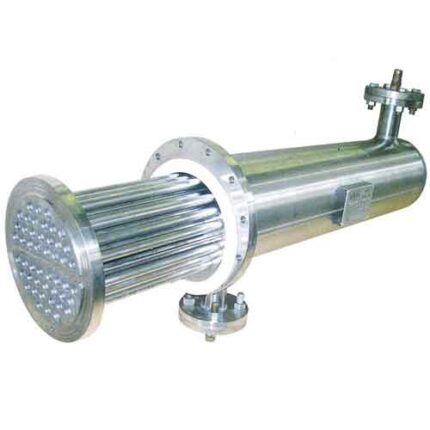
Food Industry Tubular Heat Exchangers
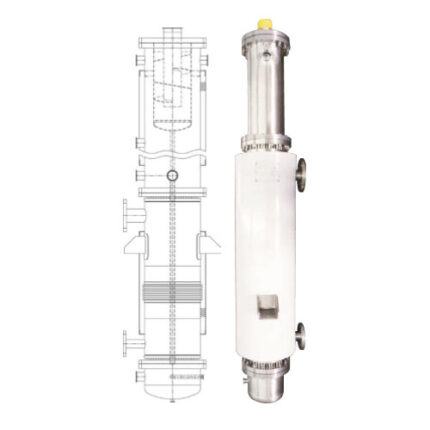
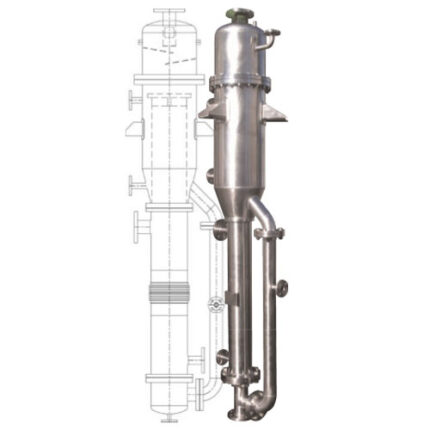
Steam Generator
Heat exchangers are devices used to change the temperature, pressure or composition of a fluid or gas. It is part of a closed system, often used in industrial processes and for heat transfer, and can be used for a variety of purposes such as temperature changes, heat recovery, or cooling or heating liquids.
Heat exchangers operate in an area where two different fluids (usually liquid or gas) come into contact with each other. One fluid transfers heat to another and thus the temperature difference is eliminated. Thus, as the temperature of one fluid increases, the temperature of the other fluid decreases.
Heat exchangers are used in industrial processes, power plants, HVAC systems and many other applications. For example, in a home's heating systems, a heat exchanger helps transfer heat from one room to another or hot water to cold water.
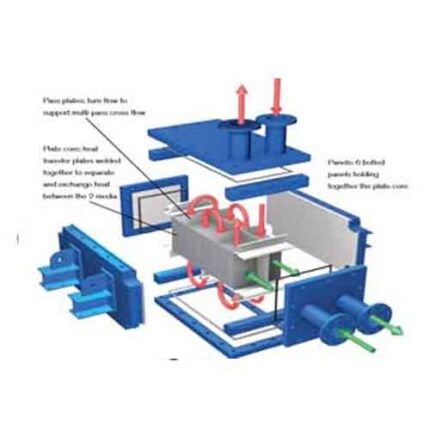
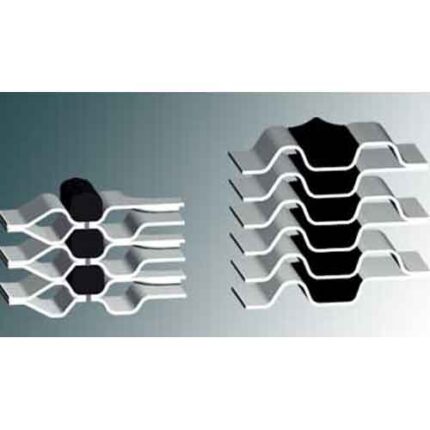
Heat exchangers can be of different types such as tubular heat exchangers, plate heat exchangers or shell-tube heat exchangers. Tube heat exchangers use a bundle of tubes through which fluids pass between two tubes, while plate heat exchangers use a series of plates through which fluids pass through spaces between thin metal plates. Shell-tube heat exchangers, on the other hand, use a tube bundle enclosed in a large shell with a tube bundle inside.
Heat exchangers are widely used in industrial processes to increase energy efficiency, reduce costs and optimize processes. For example, by using a heat exchanger, you can use hot water used in a process to heat cold water or cool hot gas. This saves energy and improves process efficiency.