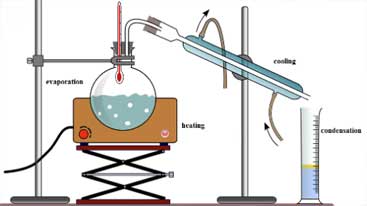
Desulfurization Process
It is the process of purifying a substance from the sulfur (SO3) contained in its composition or from a sülfür (S-2). In these processes of chemistry, we offer you reliable and quality services with our wide range of products in heating, cooling and mixing processes with our plate heat exchangers, industrial pumps and other flow equipment.
Cooling Heat Exchanger
Other Equipment That Can Be Used In The Process
Mixers
Agitators
Blenders
Stainless Steel Connection Equipment
What is the desulfurization process?
Desulfurization process is a procedure used to remove or reduce sulfur compounds (for example, hydrogen sulfide and organic sulfur compounds) in products generally derived from hydrocarbon sources such as oil and natural gas. This process is important for environmental protection, processing efficiency and product quality.
The desulfurization process is generally applied in refining or gas processing plants of hydrocarbon fluids.
The desulfurization process usually consists of the following stages:
- Desulfurization: The first step of the process is the removal or reduction of sulfur compounds from the hydrocarbon fluid. This usually involves removing gases such as hydrogen sulfide (H2S). This step is usually accomplished using gas-phase or liquid-phase chemical reactions or physical processes.
-
Sulfur Capture and Recovery: Sulfur compounds removed during the desulfurization process are often captured and used for recovery into sulfur production or other industrial applications. This step reduces waste generation during the process and results in an economically valuable by-product.
-
Product Improvement: After desulfurization, the quality and purity of hydrocarbon fluid products increases. This results in cleaner, purer products for use in a variety of industrial applications.
 The desulfurization process plays an important role in environmental protection because sulfur compounds such as hydrogen sulfide can cause environmental pollution and harm to human health when released into the atmosphere. Additionally, desulfurization helps treat hydrocarbon fluids more efficiently in processing plants and yield higher quality products. Therefore, desulfurization is widely applied in oil refineries, natural gas processing plants and other industrial facilities.
The desulfurization process plays an important role in environmental protection because sulfur compounds such as hydrogen sulfide can cause environmental pollution and harm to human health when released into the atmosphere. Additionally, desulfurization helps treat hydrocarbon fluids more efficiently in processing plants and yield higher quality products. Therefore, desulfurization is widely applied in oil refineries, natural gas processing plants and other industrial facilities.
Use of heat exchangers in desulfurization process
In desulfurization processes, exchangers are generally used for heat transfer and cooling. During desulfurization processes, heat can be generated during reactions and exchangers are used to control and manage this heat.
Some examples of the use of heat exchangers in desulfurization processes:
-
Sıcaklık Kontrolü: Kükürt giderme işlemlerinde reaksiyonlar sırasında yüksek sıcaklıklar oluşabilir. Bu durumda, eşanjörler soğutma suyu veya başka bir soğutma akışkanı aracılığıyla ısı transferini sağlayarak reaksiyon sıcaklığını kontrol edebilirler. Bu şekilde, istenmeyen reaksiyonların veya yan ürünlerin oluşması engellenir.
-
Temperature Control: High temperatures may occur during reactions in desulfurization processes. In this case, exchangers can control the reaction temperature by providing heat transfer through cooling water or another cooling fluid. In this way, the formation of undesirable reactions or by-products is prevented.
-
Lowering the Reaction Temperature: Some desulfurization processes are carried out at low temperature. Heat exchangers can lower the reaction temperature and provide the desired reaction conditions by using cooling fluid.
-
Heat Recovery: The heat generated during desulfurization processes can be recovered through exchangers. This heat recovery increases process efficiency and reduces energy costs.
-
Cooling Water Cycles: Cooling water is generally used in desulfurization processes. Heat exchangers reduce the temperature of the cooling water and ensure that the system remains constantly cold.
-
Cooling of the Reaction Medium: The reaction medium (e.g., liquid or gas) used in desulfurization processes may need to be cooled. Heat exchangers can be used to lower the temperature of the reaction medium and provide the desired reaction conditions.
In this way, exchangers are used for various functions such as temperature control, cooling and heat recovery in desulfurization processes. This increases process efficiency, reduces energy costs and helps minimize unwanted side effects during the process.
Use of mixers in desulfurization process
In desulfurization processes, mixers are generally used to increase the efficiency of the reactions and obtain a homogeneous mixture. During these processes, catalysts and chemical reagents are often added to the reaction medium and must be homogeneously distributed. Mixers increase the interaction of these catalysts and reagents with the reaction medium, increasing the efficiency of the process.
Some examples of the use of mixers in desulfurization processes:
- Catalyst Distribution: Catalysts are substances that increase the rate of a reaction or enable the reaction. Catalysts used in desulfurization processes should generally be distributed homogeneously into the reaction medium. Mixers ensure that catalysts are distributed homogeneously within the reaction medium, thus allowing the reaction to occur effectively throughout its entire volume.
-
Reagent Distribution: It is important that the chemical reagents used in desulfurization processes are distributed homogeneously into the reaction environment. This allows the reagents to interact with the sulfur compounds and the desired reactions to occur. Mixers ensure that the reagents are distributed homogeneously within the reaction medium, thus increasing the efficiency of the reaction.
-
Mixing the Reaction Medium: It is important to mix the reaction medium used in desulfurization processes homogeneously. This ensures that the reagents, catalysts and reaction products are evenly distributed and ensures that the reaction occurs homogeneously throughout the entire volume. Agitators help to obtain a homogeneous mixture by mixing the reaction medium.
As a result, in desulfurization processes, mixers ensure homogeneous mixing of the reaction medium and effective distribution of catalysts and reagents. This increases the efficiency of the reaction and results in the desired products.